分類學
| 科: | 蝙蝠科 (Vespertilionidae) |
| 屬: | 伏翼屬 (Pipistrellus ) |
| 學名: | Pipistrellus abramus (Temminck, 1838) |
| 異名: |
Vespertilio abramus Temminck, 1838, V. akokomuli Temminck, 1840, V. pumiloides Tomes, 1857 |
| 本地英文名: | Japanese Pipistrelle |
| 其他英文名: | Japanese House Bat, Javan Pipistrelle |
| 本地中文名: | 東亞家蝠 |
| 其他中文名: | 日本伏翼、家蝠 |
| 分類註釋: | - |
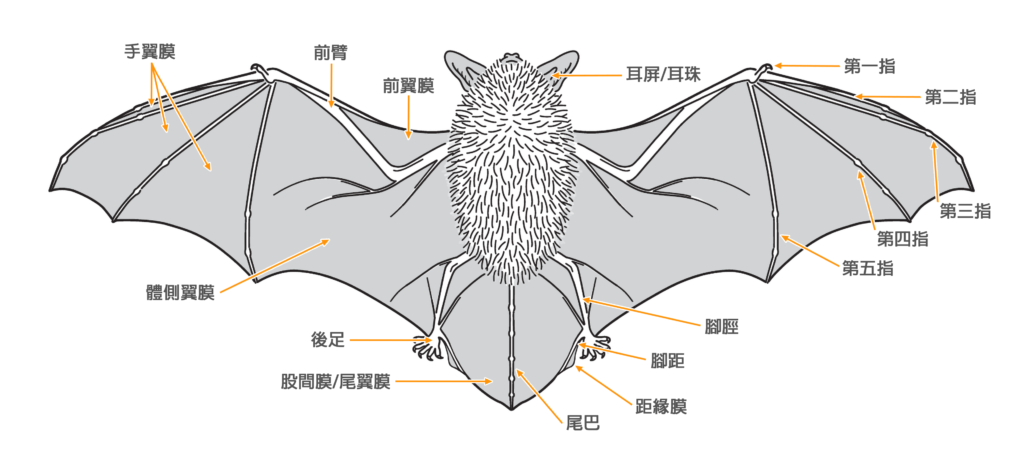
| 外形特徵 | |
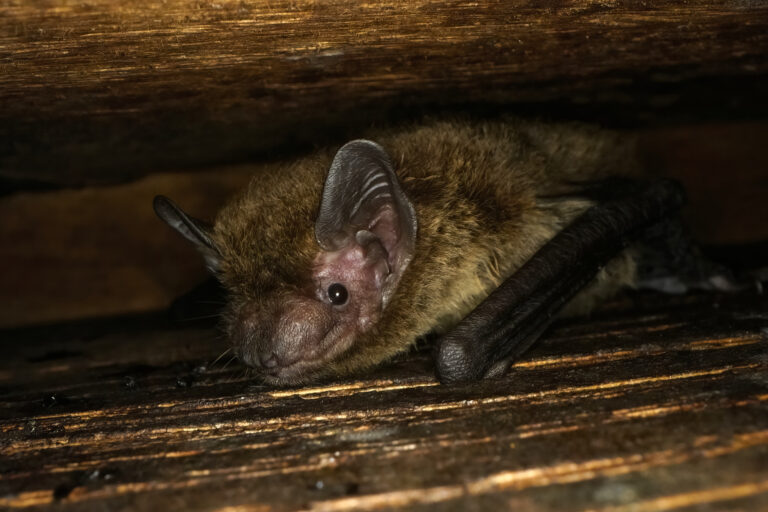
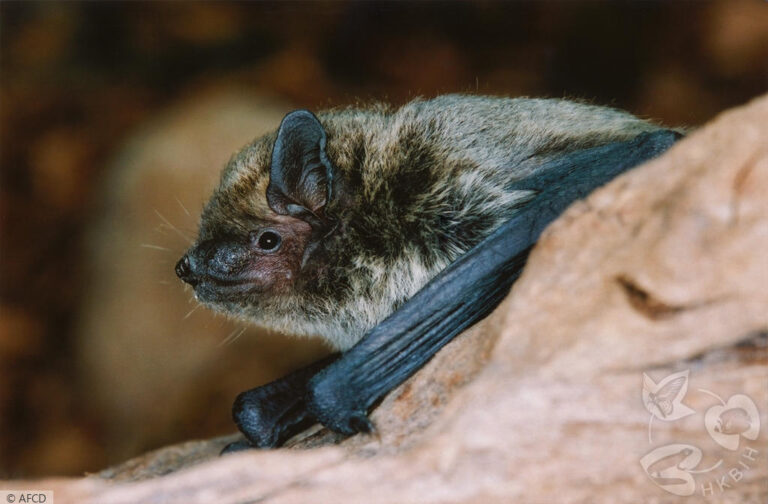
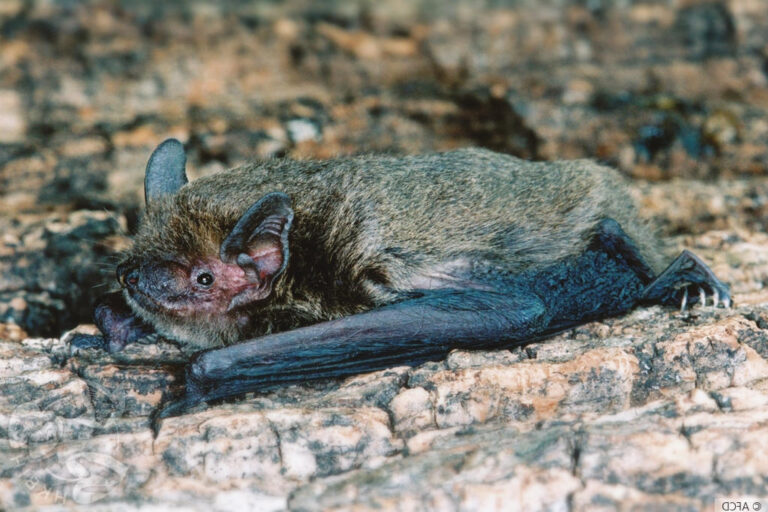
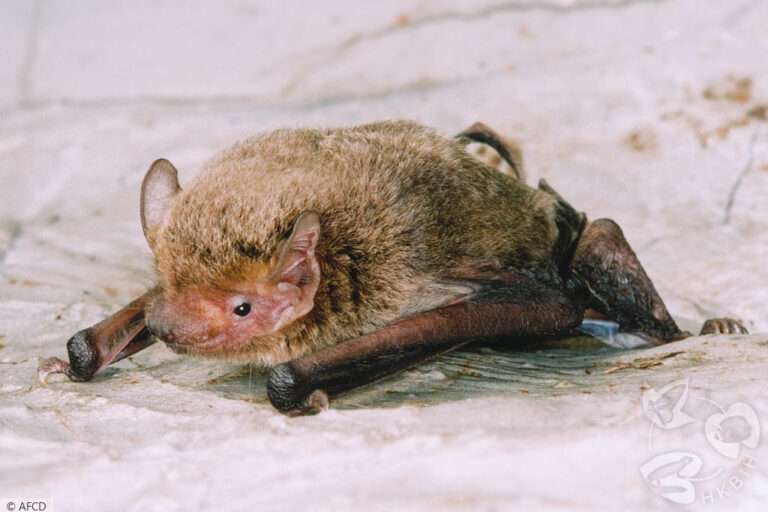
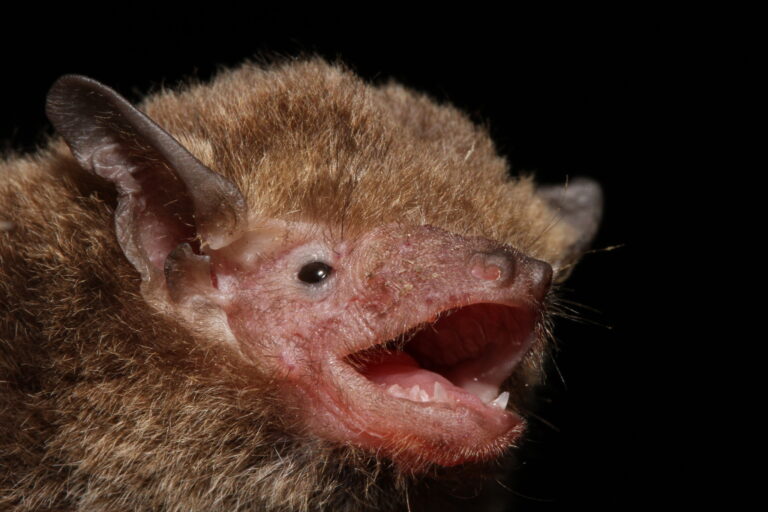
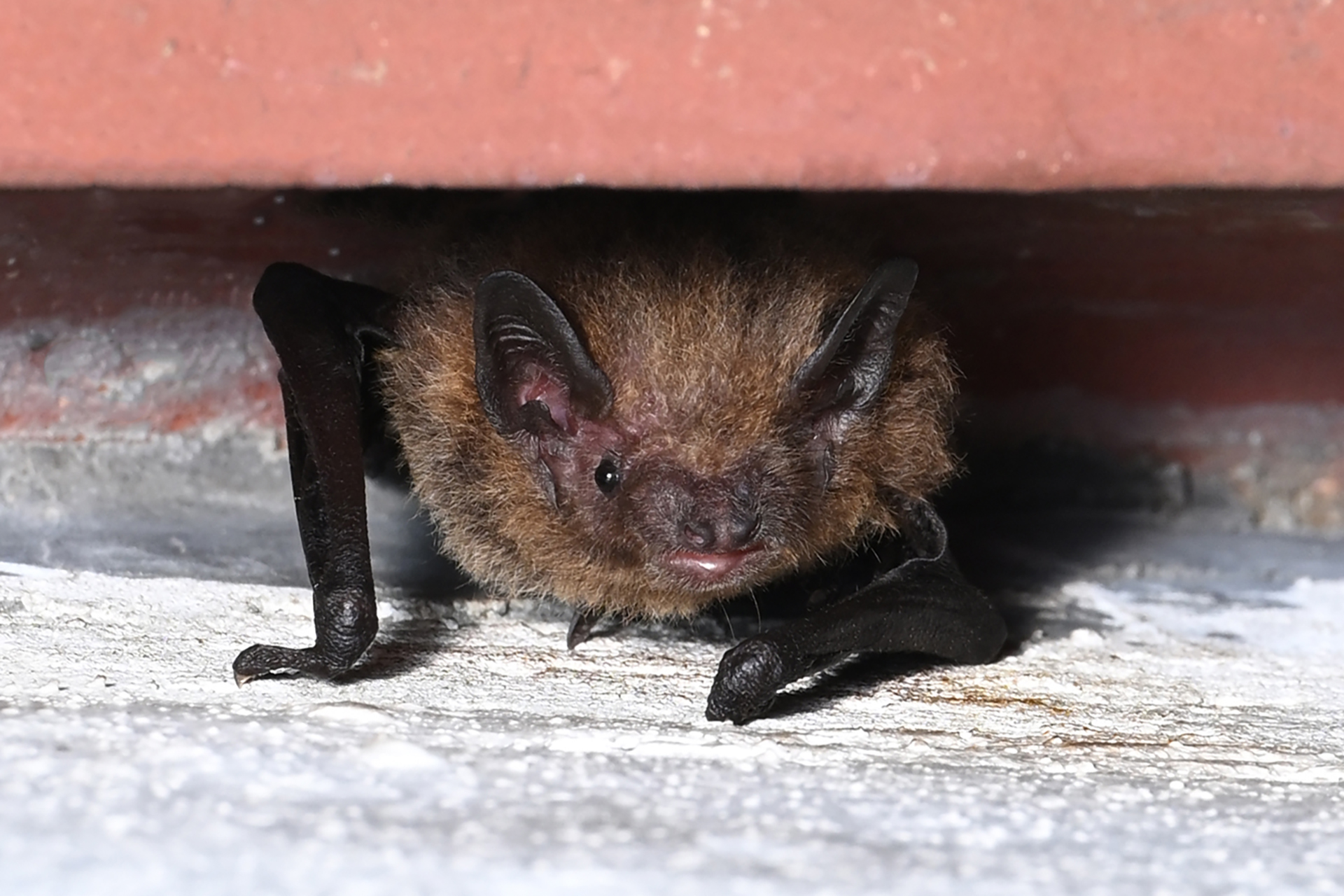
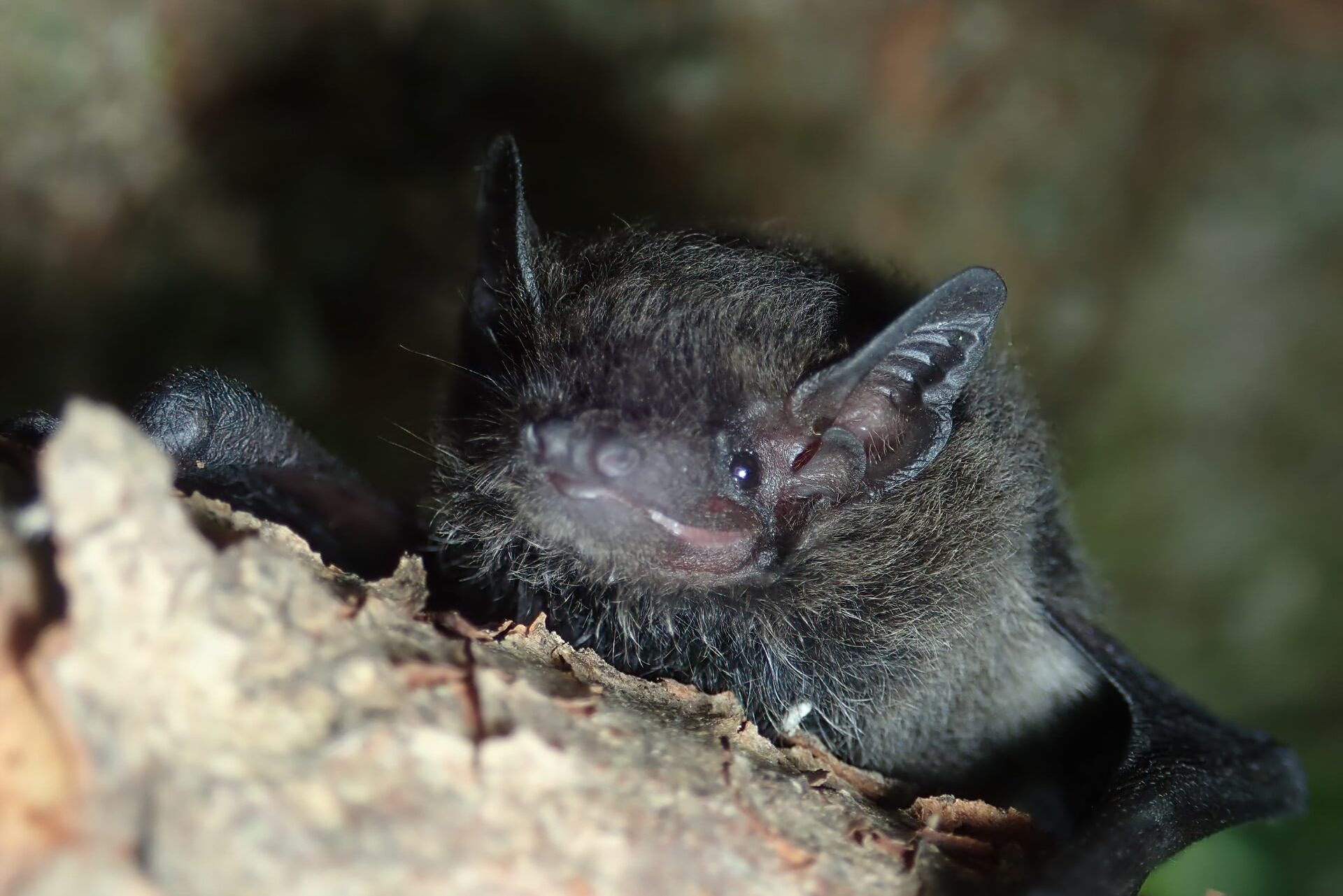
| 毛色: | 背毛顏色常見為灰褐/灰橄欖色(基部深褐色、末端灰褐或淺啡色);腹毛為灰白/淺灰褐色(基部黑褐色、末端灰白);有些個體整體較啡黃;幼蝠整體毛色較深,整體呈灰黑色 |
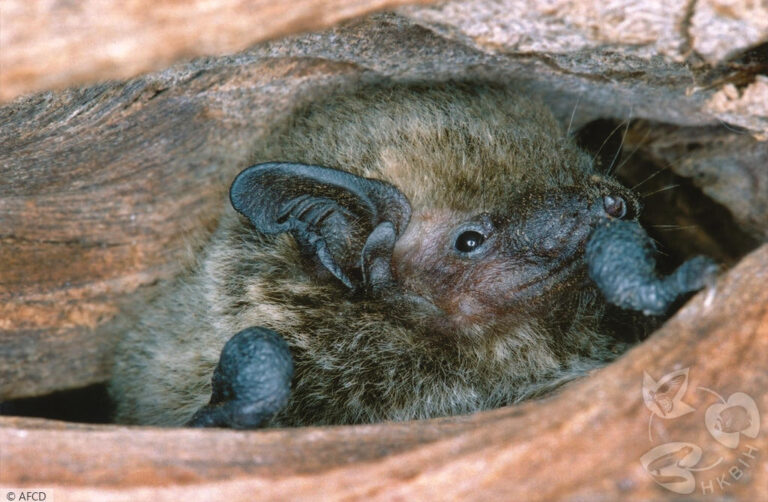
| 耳朵: | 耳殼略呈三角形,耳尖圓鈍;耳殼及耳屏顏色呈棕色,但個體間的深淺度各異;耳屏為拇指型,短窄,頂端圓鈍且向前微曲,長度約耳殼的一半 |
| 頭部: | 吻部呈棕色,但個體間的深淺度各異,兩側略顯膨大有腺體,於緊迫時可分泌啡黃色液體;臉部及眼周裸露皮膚一般呈肉色 |
| 四肢: | 後足較小,翼膜連接至趾基 |
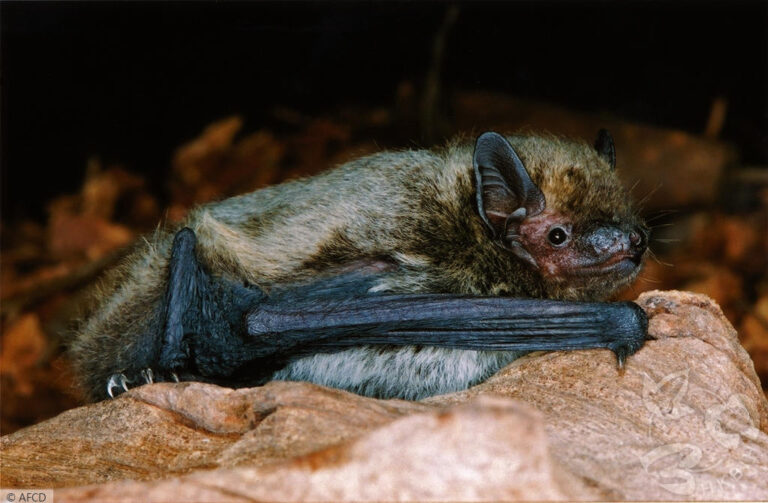
| 尾部: | 尾長,完全被股間膜包裹,末端(< 1 mm)略微突出於股間膜;腳距長,由足踝延伸至尾膜後緣之半,具發達的距緣膜,膜中央具明顯的橫軟骨隔膜 |
| 陰莖: | 陰莖長而明顯(9.1 - 12.7 mm);陰莖骨呈S形(> 9 mm) |
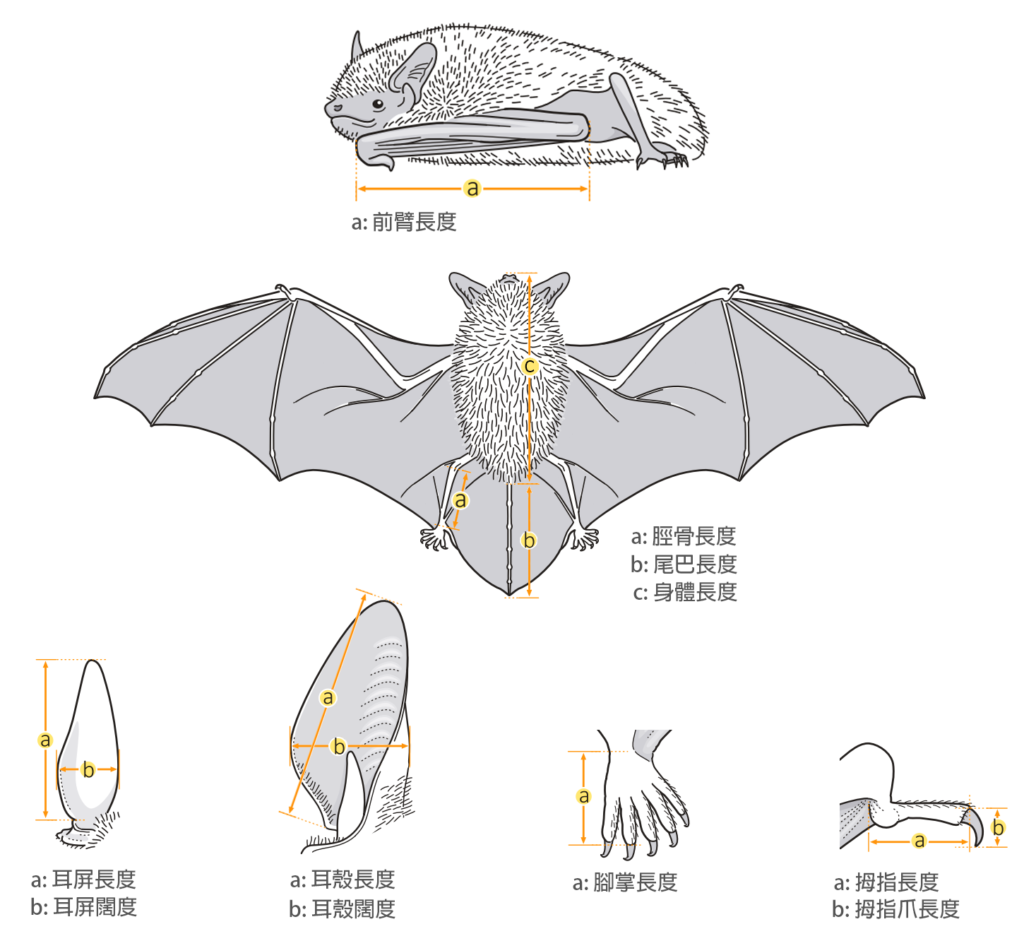
| 體形及體重測量 | |
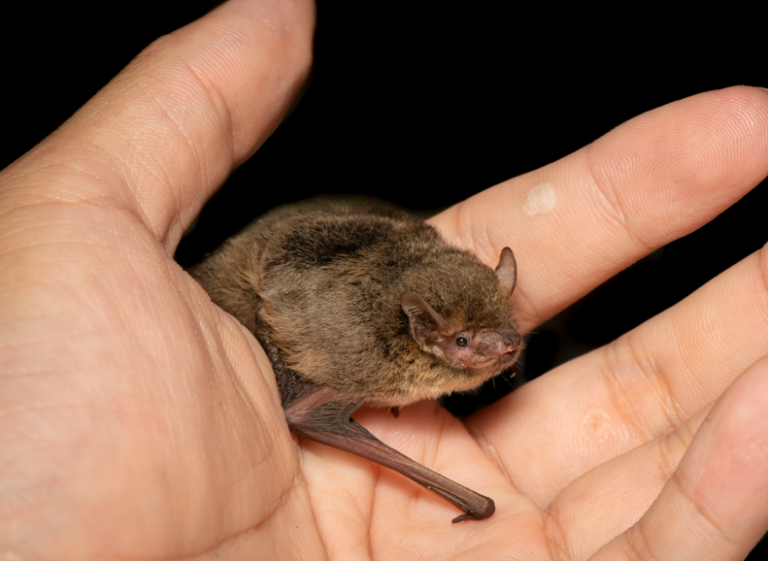
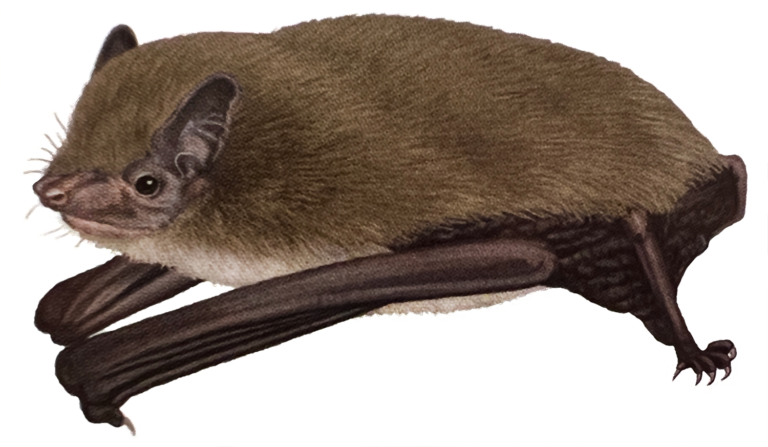
| 體型: | 小型伏翼蝠 |
| 軀幹: | 38.0 - 60.0 mm |
| 尾長: | 27.0 - 45.0 mm |
| 耳長: | 8.0 - 13.0 mm |
| 後足: | 6.0 - 10.0 mm |
| 前臂: | 29.0 - 36.0 mm |
| 體重: | 3.8 - 5.8 g |
| 翼形參數(雌蝠) | |
| 翼長: | 0.109 m |
| 翼面積: | 0.004 m2 |
| 翼載: | 16.30 ± 2.00 N/m2 (高) |
| 翼展比: | 4.00 ± 0.30 (低) |
| 翼尖指數: | 2.00 ± 0.50 (高) |
| 參考資料: | Shao et al., 2014 |
生態資料
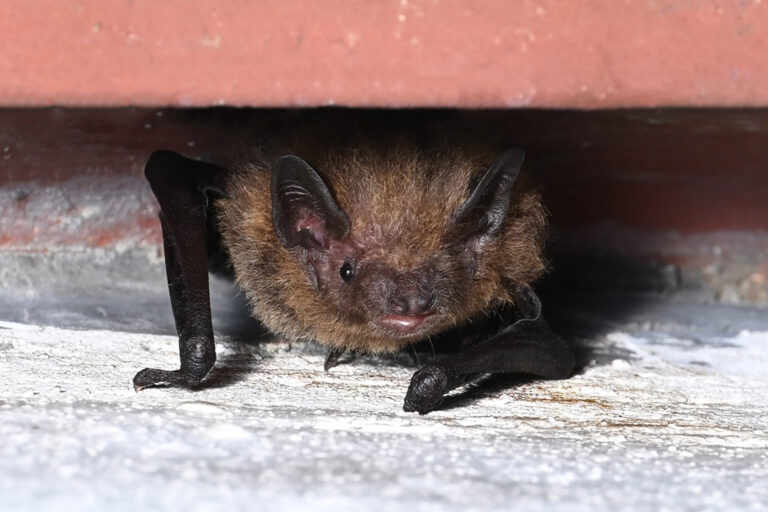
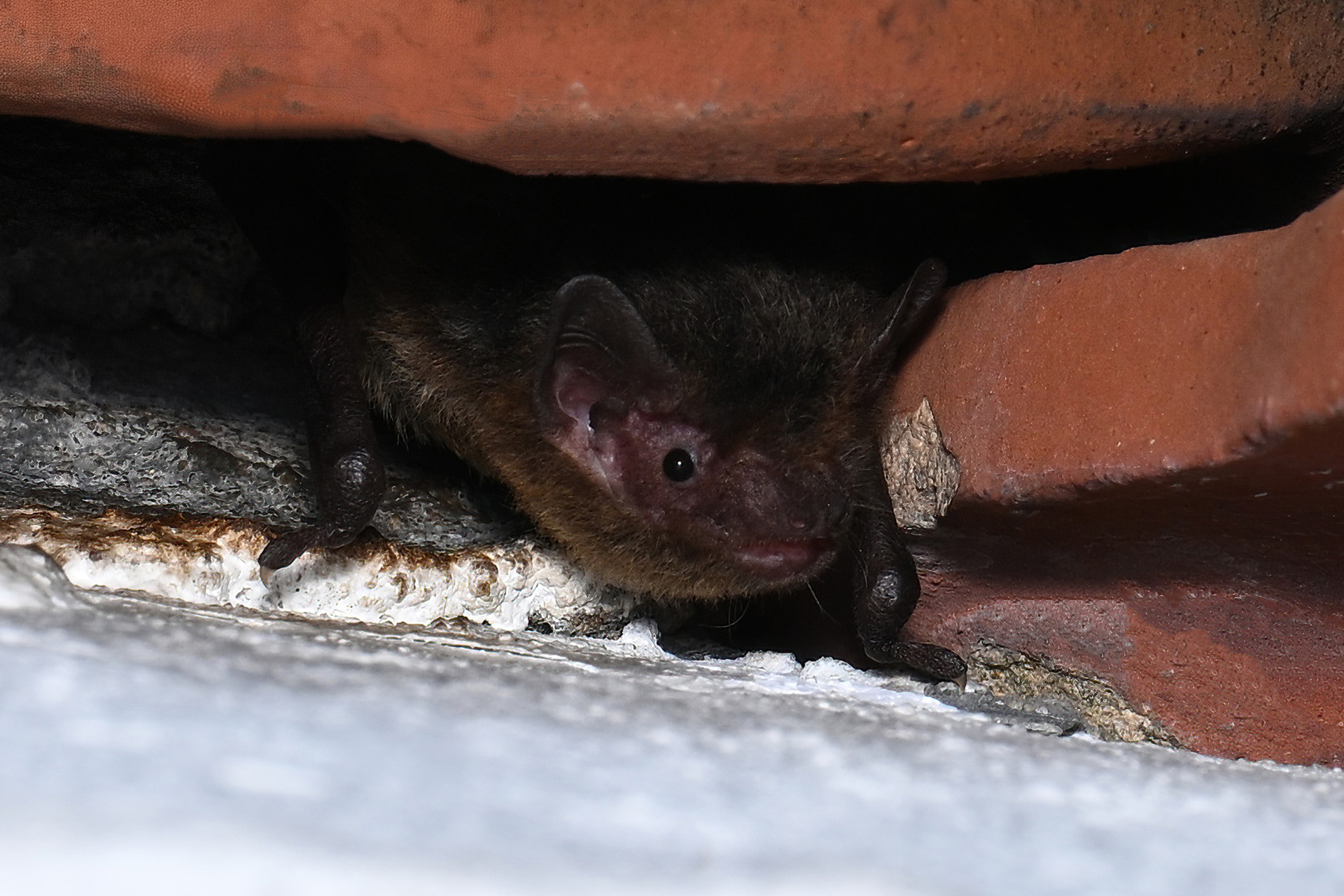
| 生境: | 適應性很強的蝙蝠,能棲息於多種生境,包括林區、鄉郊及市區。主要棲身於建築物的隙縫(樓頂、屋簷、女兒牆、牆洞、牆隙和窗隙等)及電器或工具的狹縫(抽氣扇、冷氣機、太陽傘及鐵通等),亦可棲息於蝙蝠箱。此外,亦有棲息在洞穴及金腰燕燕巢(Cecropis daurica)的國外紀錄。 |
| 習性: | 習慣群棲,群落大小視乎棲所大小而定,獨棲的個體一般棲息於狹窄縫隙,而較大的群落會選擇空間較大的棲所(如蝙蝠箱、女兒牆等)。群落平均由20隻個體組成,日本最高曾記錄得250隻。繁殖季的育幼群落一般較大型,幼蝠初生時的群落約1-110隻。雌蝠會與幼蝠常年共棲,而雄蝠一般會獨棲。 |
| 繁殖: | 本地群落的生產期在5-6月,不同群落的生產期各異,一般約於5月中上旬分娩,幼蝠在8月下旬斷奶。每胎2-3隻幼蝠,但死亡率甚高,在斷奶前通常僅一半幼蝠存活,在斷奶後至一歲期間亦有約20%(雌性)及約90%(雄性)的死亡率。 |
| 壽命: | 壽命較短,雄蝠一般1-3年,雌蝠4-5年。 |
| 冬眠: | 在日本的群落會在溫度較低時(約16-20°C)會減少飛出及活動時間,在15°C或以下或在大雨時極少飛出,如低溫持續時則會進入冬眠周期。不過,在台灣及香港,牠們全年活躍不冬眠,但活躍程度會因應天氣溫度及食物來源而變化。本地群落在冬季(12-2月)溫度較低時仍會出飛覓食,但出巢次數及活動時間會明顯減少。 |
| 飛行: | 飛行速度快速,靈活性及空中盤旋能力亦較好,但飛行效率偏低,適合中距離飛行。 |
| 覓食: | 屬全晚活動型蝙蝠,在傍晚日落前10-30分鐘飛出日間棲所,外出覓食,飛出時間受附近光度影響,天陰時會較早飛出。每晚會有兩次外出覓食高峰期,分別在日落後(3小時或以上)及黎明前(1小時或以上),期間會在不同的夜間棲所短暫休息。在不同開闊生境都可觀察到牠們飛行覓食(市區公園、農地、漁塘、荒地、林區、濕地、水塘、河溪等等),習慣以打圈方式盤旋覓食;通常在樹冠層、灌木叢、水體上方或圍繞著街燈盤旋覓食。其活動範圍甚廣,部分個體會先在棲所附近覓食,其後再飛到較遠的覓食地,曾有飛離棲所5 km覓食的記錄。 |
| 食性: | 食蟲性蝙蝠,於空中捕食昆蟲;廣食性蝙蝠,食源涵盖了12個目的昆蟲及蜘蛛,牠會隨著食源變化(生境及季節因素)而調整其捕食策略。例如:日本市區中的群落會主要捕食鱗翅目、雙翅目及半翅目;在米田的則主要捕食雙翅目、半翅目及膜翅目。 |
台灣東亞家蝠食性
日本東亞家蝠食性
分布概況及自然度
| 本地分布: | 新界、香港島及大嶼山 |
| 全球分布: | 中國中、東和南部(包括海南島)、台灣、緬甸北部、老撾北部、越南北部和中部(包括吉婆島和凱蒂恩島)、俄羅斯烏蘇里地區、北韓、南韓、日本(包括附近許多島嶼)、俄羅斯烏蘇里地區(庫頁島有一尚待確認的記錄);印度北、南和東北部有零散記錄 (Moratelli et al., 2019) |
本地分布地圖
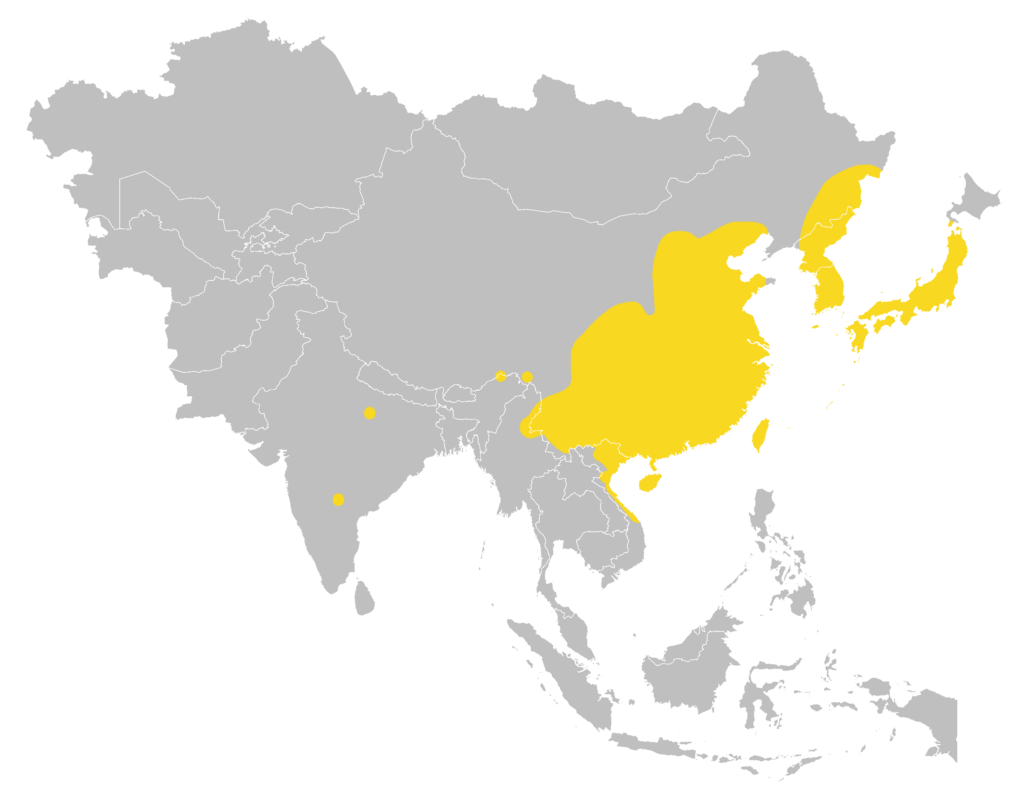
全球分布地圖
(Moratelli et al., 2019)
本地狀況及載列名錄
| 首次記錄: | 1955年 |
| 物種來源: | 原生 |
| 本地現況: | 十分常見 (Shek & Chan, 2006) |
| 國內現況: | 無危 (中國脊椎動物紅色名錄) |
| 全球現況: | 無危 (IUCN紅色名錄) |
| 潛在威脅: | 待續 |
回聲定位
如有需要,請先註冊會員,並以電郵方式聯絡小蝙申請閱讀權限。
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Call structure | FM/QCF |
| Duration | 3.50 ± 0.38 ms |
| Inter pulse interval | 46.83 ± 17.49 ms |
| Peak frequency | 58.10 ± 3.80 kHz |
| Highest frequency | 78.00 ± 5.72 kHz |
| Lowest frequency | 45.86 ± 1.57 kHz |
| 錄音地區: | 中國貴州省 |
| 錄音方式: | 飛行帳蓬 |
| 參考資料: | 馮江等,2003 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Call structure | FM/QCF |
| Duration | 2.60 ± 0.80 ms |
| Inter pulse interval | 71.00 ± 36.50 ms |
| Peak frequency | 52.10 ± 2.40 kHz |
| Highest frequency | 86.60 ± 10.20 kHz |
| Lowest frequency | 43.40 ± 10.60 kHz |
| 錄音地區: | 中國湖北省(武漢) |
| 錄音方式: | 人手放飛 |
| 參考資料: | Luo et al ., 2007 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Call structure | FM/QCF |
| Duration | 6.78 ± 7.91 ms |
| Inter pulse interval | 97.77 ± 26.36 ms |
| Peak frequency | 45.52 ± 1.09 kHz |
| Highest frequency | 62.96 ± 5.81 kHz |
| Lowest frequency | 43.53 ± 0.94 kHz |
| 錄音地區: | 中國河北省(北京) |
| 錄音方式: | 人手放飛 |
| 參考資料: | Ma et al ., 2010 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Call structure | FM/QCF |
| Duration | 3.30 ± 1.10 ms |
| Inter pulse interval | 63.70 ± 38.6 ms |
| Peak frequency | 56.30 ± 6.60 kHz |
| Highest frequency | 87.70 ± 9.80 kHz |
| Lowest frequency | 47.40 ± 4.80 kHz |
| 錄音地區: | 中國浙江省(舟山) |
| 錄音方式: | 飛行帳蓬 |
| 參考資料: | Shao et al., 2014 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Call structure | FM/QCF |
| Duration | 5.97 ± 1.53 ms |
| Inter pulse interval | 82.68 ± 9.49 ms |
| Peak frequency | - |
| Highest frequency | 53.30 ± 5.30 kHz |
| Lowest frequency | 46.74 ± 1.94 kHz |
| 錄音地區: | 台灣 |
| 錄音方式: | 野生叫聲 |
| 參考資料: | 趙念民,2001 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Call structure | FM/QCF |
| Duration | - ms |
| Inter pulse interval | - ms |
| Peak frequency | - kHz |
| Highest frequency | - kHz |
| Lowest frequency | - kHz |
| 錄音地區: | 香港 |
| 錄音方式: | TBC |
| 參考資料: | TBC |
相似物種
小伏翼
Pipistrellus tenuis
體型:三者中最細小
前臂:25.0 - 31.0 mm
體毛:毛短,背毛呈均勻棕褐/黑褐色(末端略淡)
耳殼:三角形,深棕色
耳屏:較修長,頂端圓鈍且向前微曲
吻部:深啡至灰黑色,兩側明顯膨大
尾巴:末端(<1 mm)略微突出於股間膜
陰莖:陰莖較短(3.8 mm)
東亞家蝠
Pipistrellus abramus
體型:較小伏翼大,與灰伏翼相若或較小
前臂:29.0 - 36.0 mm
體毛:毛短,背毛呈灰褐色(未端灰褐色)
耳殼:三角形,可呈不同程度的棕色
耳屏:較修長,頂端圓鈍且向前微曲
吻部:深啡至灰黑色,兩側略顯膨大
尾巴:末端(<1 mm)略微突出於股間膜
陰莖:陰莖長而明顯(9.1 - 12.7 mm)
參考資料
Chung, C. U., Kim, S. C., Jeon, Y. S., & Han, S. H. (2017). Changes in habitat use by female Japanese Pipistrelles (Pipistrellus abramus) during different stages of reproduction revealed by radio telemetry. Journal of Environmental Science International, 26(7), 817-826.
Funakoshi, K., & Uchida, T. (1978). Studies on the physiological and ecological adaptation of temperate insectivorous bats: III. Annual activity of the Japanese house-dwelling bat, Pipistrellus abramus. Journal of the Faculty of Agriculture, Kyushu University, 23(1/2), 95-115.
Funakoshi, K., & Uchida, T. (1982). Age composition of summer colonies in the Japanese house-dwelling bat, Pipistrellus abramus. Journal of the Faculty of Agriculture, Kyushu University, 27(1/2), 55-64.
Funakoshi, K., Katahira, R., & Ikeda, H. (2009). Night-roost usage and nocturnal behavior in the Japanese house-dwelling bat, Pipistrellus abramus. Mammal study, 34(3), 131-139.
Hirai, T., & Kimura, S. (2004). Diet composition of the common bat Pipistrellus abramus (Chiroptera; Vespertilionidae), revealed by fecal analysis. Japanese Journal of Ecology, 54, 159-163.
Hughes, A. C., Satasook, C., Bates, P. J. J., Soisook, P., Sritongchuay, T., Jones, G., & Bumrungsri, S. (2011). Using Echolocation Calls to Identify Thai Bat Species: Vespertilionidae, Emballonuridae, Nycteridae and Megadermatidae. Acta Chiropterologica, 13(2), 447–455.
Jeyapraba, L., Margaret, I. V., Addline, D., & Sakthi, V. (2023). Prediction of foraging strategy of insectivorous bats through their wing morphology. Journal of Survey in Fisheries Sciences, 10(3S), 1903-1917.
Jayaraj, V. K., Tahir, N. A., Udin, N. A., Baharin, N. K., Ismail, S. K., & Zakaria, S. N. A. (2012). Species diversity of small mammals at Gunung Stong state park, Kelantan, Malaysia. Journal of Threatened Taxa, 4(6), 2617-2628.
Jiang, Z. G., Jiang, J. P., Wang, Y. Z., Zhang, E., Zhang, Y. Y., Li, L. L., Xie, F., Cai, B., Cao, L., Zheng, G. M., Dong, L., Zhang, Z. W., Ding, P., Luo, Z. H., Ding, C. Q., Ma, Z. J., Tang, S. H., Cao, W. X., Li, C. W., Hu, H. J., Ma, Y., Wu, Y., Wang, Y. X., Zhou, K. Y., Liu, S. Y., Chen, Y. Y., Li, J. T., Feng, Z. J., Wang, Y., Wang, B., Li, C., Song, X. L., Cai, L., Zang, C. X., Zeng, Y., Meng, Z. B., Fang, H. X., & Ping, X. G. (2016). Red List of China’s Vertebrates. Biodiversity Science 24(5), 500‑551.
Lee, Y. F., & Lee, L. L. (2005). Food Habits of Japanese Pipistrelles Pipistrellus abramus (Chiroptera: Vespertilionidae) in Northern Taiwan. Zoological Studies, 44(1), 95-101.
Liu, S. Y., Wu, Y., & Li, S. (2022). Handbook of the mammals of China (3rd ed.). The Straits Publishing & Distribution Group.
Luo, F., Ma, J., Li, A. A., Wu, F. J., Chen, Q. C., & Zhang, S. Y. (2007). Echolocation calls and neurophysiological correlations with auditory response properties in the inferior colliculus of Pipistrellus abramus (Microchiroptera: Vespertilionidae). Zoological Studies, 46(5), 622-630.
Ma, J., Jones, G., Zhu, G. J., & Metzner, W. (2010). Echolocation behaviours of the Japanese pipistrelle bat Pipistrellus abramus during foraging flight. Acta Theriologica, 55(4), 315-332.
Moratelli, R., Burgin, C., Cláudio, V., Novaes, R., López-Baucells, A., & Haslauer, R. (2019). Vespertilionidae. In Mittermeier, R. A., & Wilson, D. E. (Eds.), Handbook of the Mammals of the World – Volume 9 Bats. (pp. 716-981). Lynx Edicions.
Morii, R. (1993). Horizontal distribution of Pipistrellus abramus in Kagawa Prefecture, Japan. Kagawa-seibutu, 20, 1-5.
Shao, W. W., Wei, L., Hu, K. L., Lin, Z. H., & Zhang, L. B. (2014) Wing morphology, echolocation calls and emergence time of Pipistrellus abramus. Acta Theriologica Sinica, 34(3), 245-251.
Shek, C. T. (2006). A Field Guide to the Terrestrial Mammals of Hong Kong. Friends of country park and cosmos book limited.
Shek, C. T., & Chan, C. S. M. (2006). Mist Net Survey of Bats with Three New Bat Species Records for Hong Kong. Hong Kong Biodiversity, 11, 1-7.
Taniguchi, K., Minegishi, H., & Kinoshita, A. (1990). Ecological data on common Japanese pipistrelle (2). Memoir of Kawasaki City Museum for Youth, 1, 23-28.
Tong, C. P. (2016). Distribution and preference of landscape features and foraging sites of insectivorous bats in Hong Kong urban parks. [Master’s thesis, The University of Hong Kong].
Yasui, S., Maruyama, N., & Kanzaki, N. (1997). Roost site selection and colony size of the common Japanese Pipistrelle (Pipistrellus abramus) in Fuchu, Tokyo. Wildlife Conservation Japan, 2(2), 51-59.
馮江、劉穎、陳敏、李振新、張喜臣、周江(2003)。普通伏翼蝠(Pipistrellus abramus)迴聲定位及母嬰交流行為研究。自然科學進展,13(12),1247-1252。
趙念民(2001)。利用回聲定位叫聲特性鑑別東亞家蝠、摺翅蝠、台灣葉鼻蝠和台灣小蹄鼻蝠之研究〔碩士論文〕。國立中山大學生物科學系。
Hong Kong Bat Radar. (19/10/2024). A Field Guide to Bats of Hong Kong: Japanese Pipistrelle (Pipistrellus abramus ). https://hkbatradar.com/en/pipistrellus_abramus