- Hong Kong Bat Radar
- Horsfield’s bat (Myotis horsfieldii)
Horsfield's Myotis
Myotis horsfieldii (Temminck, 1840)
Taxonomy
| Family: | Vespertilionidae |
| Genus: | Myotis |
| Scientific name: | Myotis horsfieldii (Temminck, 1840) |
| Synonyms: |
Leuconoe peshwa  Thomas, 1915, Myotis jeannei (Hill, 1983), Vespertilio horsfieldi  Temminck, 1840 |
| Common name: | Horsfield's Myotis |
| Other name: | Horsfield's Bat, Common Asiatic Myotis, Lesser Large-tooth Bat |
| Remark: | M. horsfieldii includes five known sub-species:M. h. horsfieldii (Tomes, 1840), M. h. deignani (Shamel, 1942), M. h. dryas (K. Andersen, 1907), M. h. jeanne (E. H. Taylor, 1934) and M. h. peshwa (Thomas, 1915). According to geographic distribution, the local species is M. h. deignani. |
| Characteristics | |
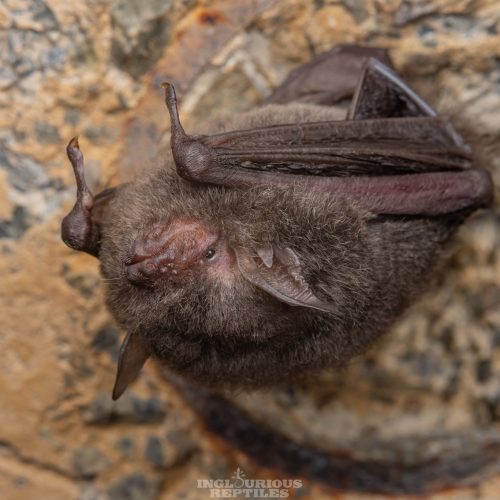
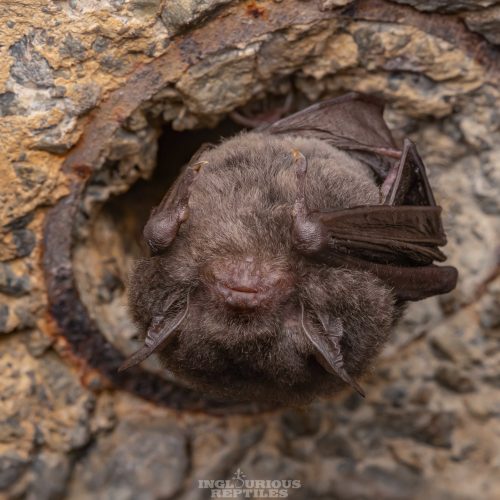
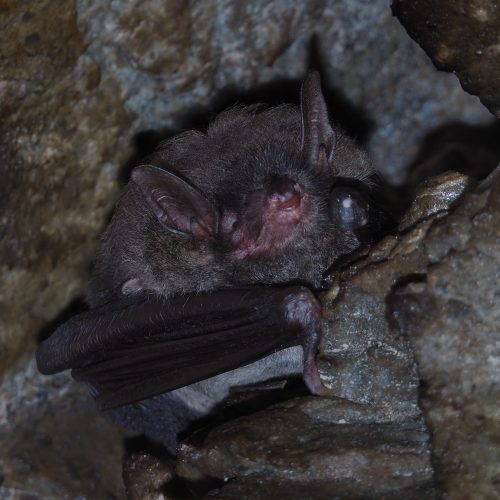
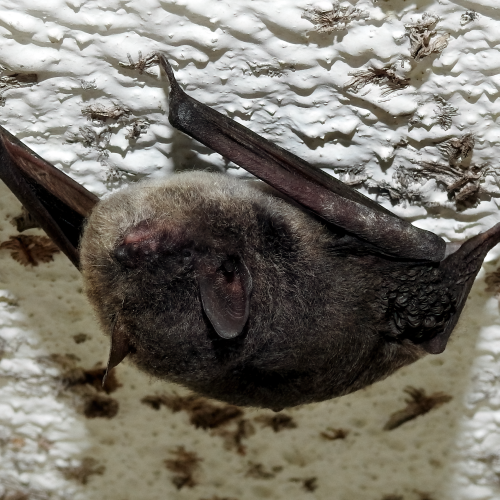
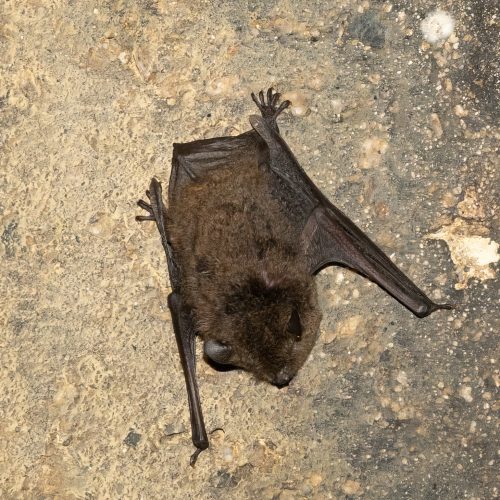
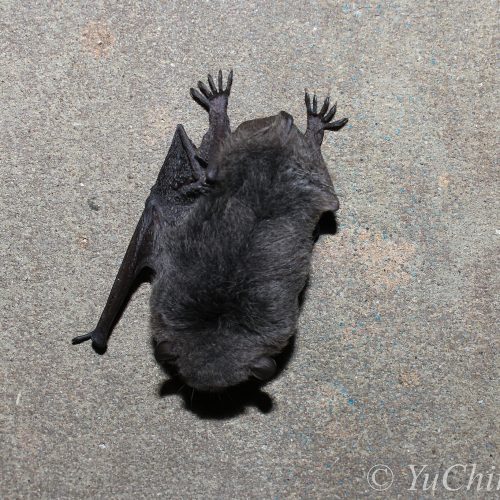
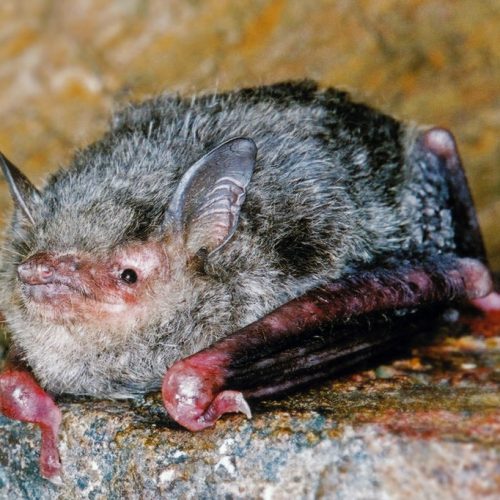
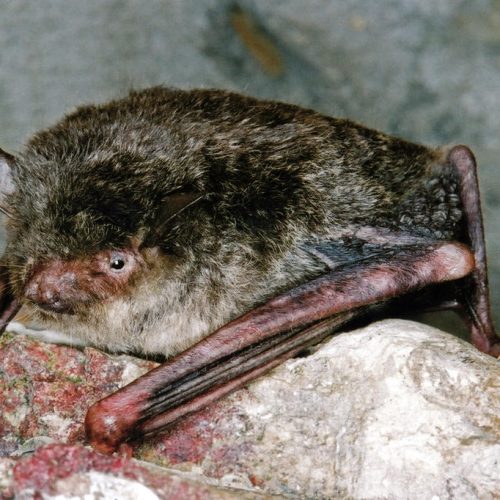
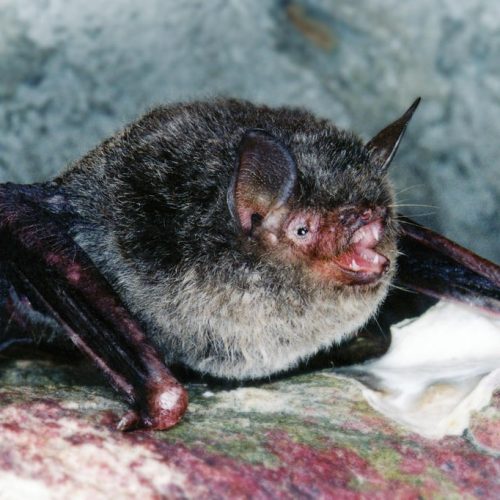
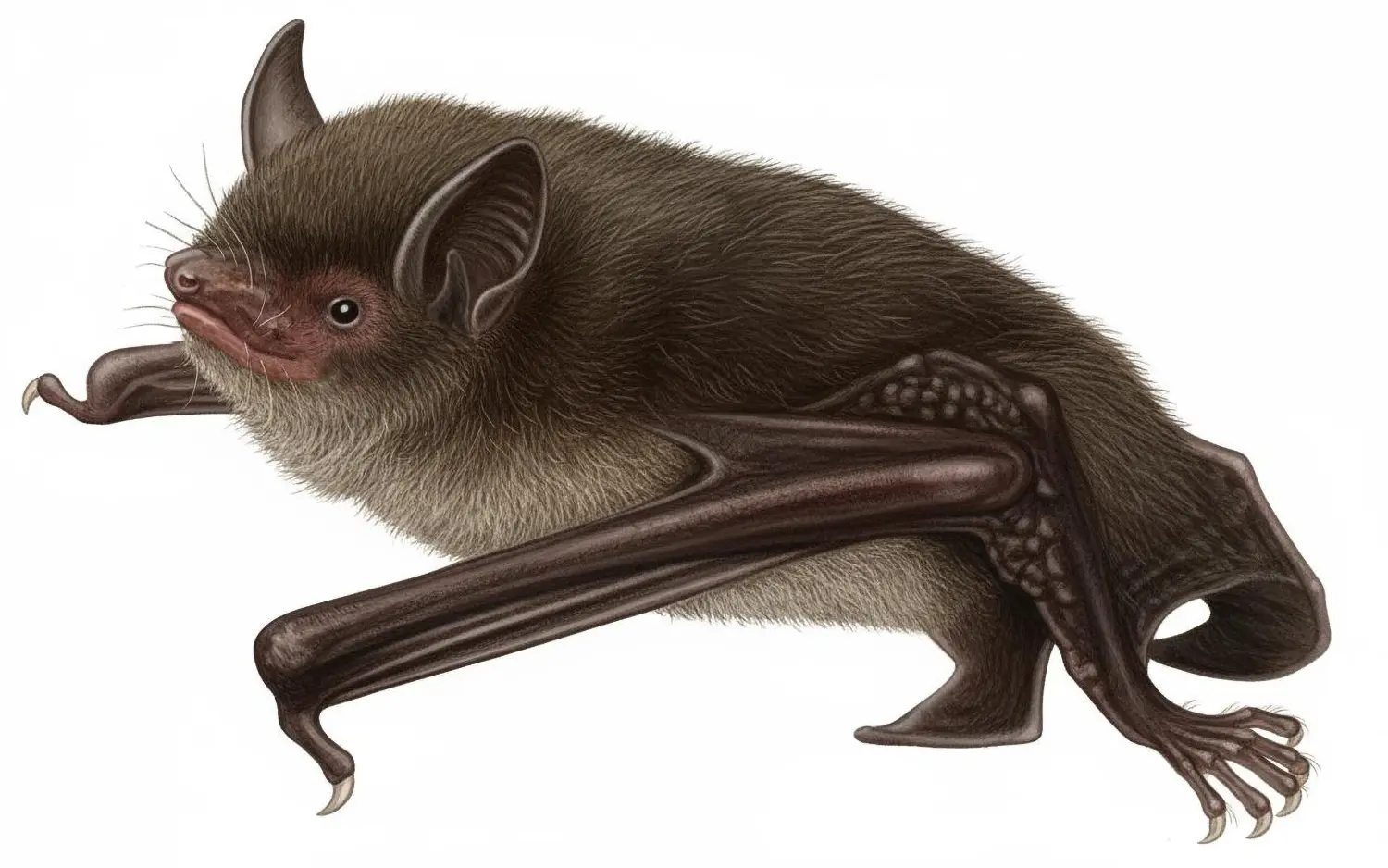
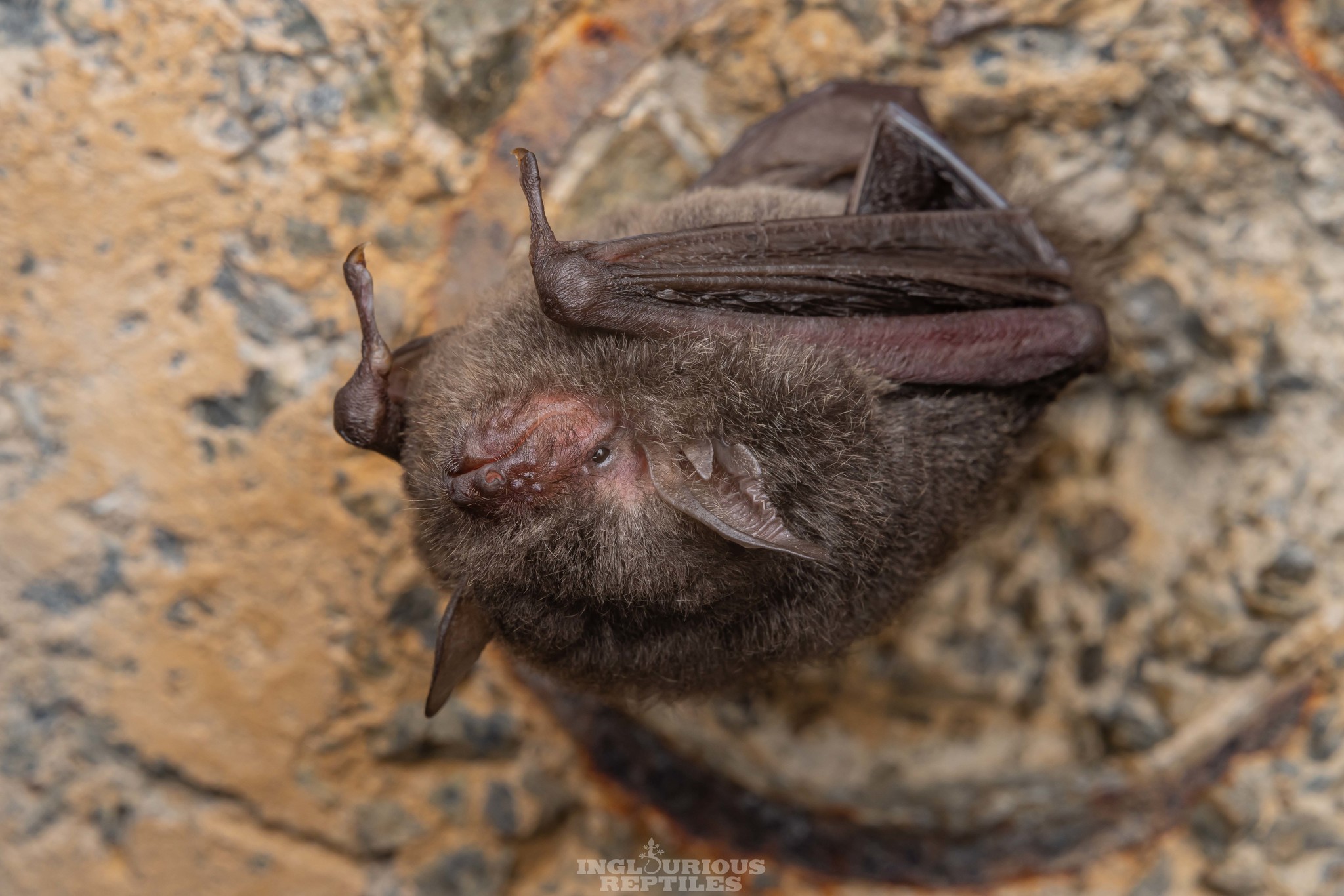
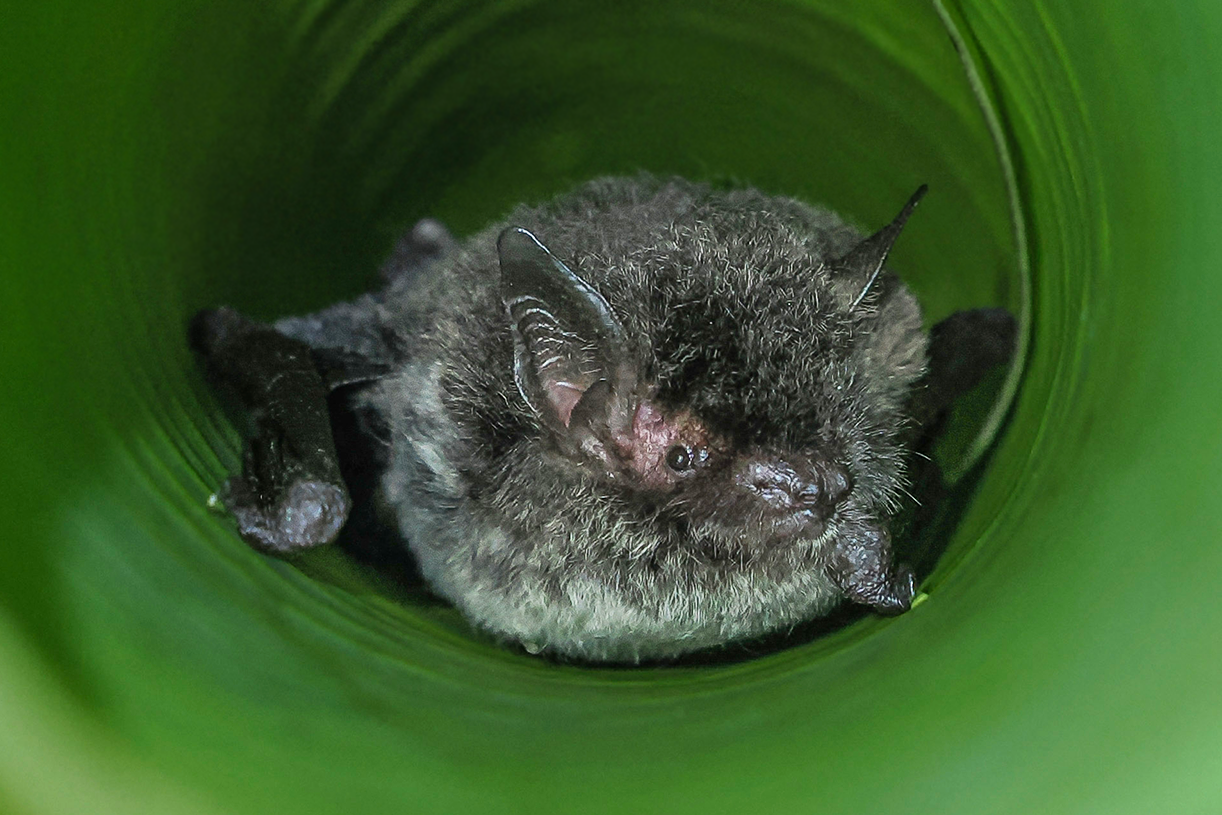
| Color: | The fur is soft and dense. The dorsal fur exhibits a mottled dark gray-brown coloration, with three distinct sections: a deep brown base, a midsection of brown, and a light beige tip. The ventral fur ranges from gray-white to dark gray, with the base being dark gray to black and the tips white to gray-white. There is considerable variation in fur coloration among individuals, with some leaning towards gray and others towards brown. Juveniles generally have a darker overall fur color, appearing gray-black. |
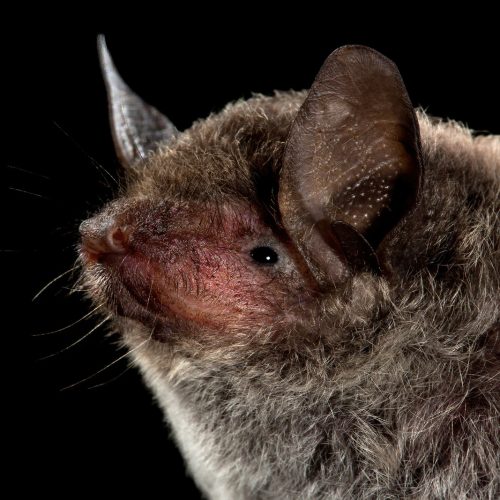
| Ear: | The ear pinna is elongated and relatively large. The anterior margin of the ear pinna forms a curved arc, slightly narrowing towards the upper sections of the anterior and posterior margins. Both the ear pinna and tragus are dark brown to gray-black in color. The tragus is slender, elongated, and narrow, measuring less than half the length of the ear pinna. |
| Head: | The muzzle typically bears whiskers, and the skin around the eyes and face is exposed and pink in color. |
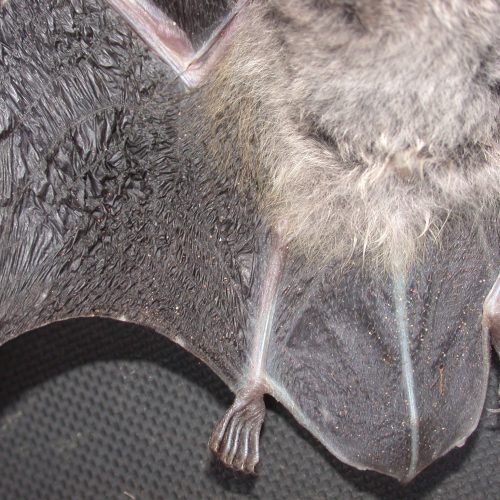
| Limbs: | The hind feet are relatively large, with a length exceeding half of the tibia. The toes have sparse, long hair, and the claws are slender, curved, and sharp, appearing translucent. The wing membranes attache to the base of the toes, approximately 2 mm away from the ankle. |
| Tail: | The tail is long and completely enveloped by the interfemoral membrane, with the tip slightly protruding beyond the membrane. The calcar is unkeeled and over halfwary to tail from ankle. |
| Body measurements | |
| Size: | Small myotis |
| Body: | 44.0 - 51.0 mm |
| Tail: | 33.0 - 43.0 mm |
| Ears: | 13.5 - 17.0 mm |
| Hind foot: | 7.0 - 11.0 mm |
| Forearm: | 33.8 - 41.5 mm |
| Weight: | 5.0 - 7.5 g |
| Wing morphology | |
| Wing span: | - |
| Wing area: | - |
| Wing loading: | 10.0 N/m2 (Medium) |
| Aspect ratio: | 2.0 (Low) |
| Tip-shape index: | - |
| Reference: | Tanalgo et al., 2012 |
Ecology
| Habitat: | This species is a cave-dwelling bat that are capable of inhabiting various habitats, including forested areas, rural landscapes, and urban environments. They exhibit a preference for well-watered woodland or wetland habitats, where they can roost in rock crevices, water conduits, culverts, under bridges, and within buildings, often seeking shelter in dry crevices or drains within these structures. |
| Habit: | They are generally solitary or form small colonies of 2-5 individuals. A single roosting site can accommodate over 100 individuals. |
| Reproduction: | The breeding season occurs from May to June, with females giving birth to one or two offspring. Typically, they produce one offspring per breeding season. |
| Hibernation: | They enter hibernation from late December to February. The duration of hibernation varies depending on the temperature. |
| Flight: | They have a moderate flight speed and excellent maneuverability, but their flight efficiency is not high, making them more suitable for medium-distance flights. |
| Foraging: | They typically forage by circling and hawking for insects just above open water surfaces, including ponds, fish ponds, lakes, aquaculture fields, and artificial/natural waterways. During flight, they generally maintain an altitude of approximately 10 cm above the water surface, capturing insect prey above the water's surface. Additionally, they may hunt in open airspaces near forest edges and along streams at low elevations above ground level. |
| Diet: | They are insectivorous bats. |
Distribution
| Local: | The New Territory, Hong Kong Island and Lantau Island |
| Global: | |
| M. h. horsfieldii | Peninsular Malaysia (including Langkawi and Penang Islands), Singapore, Borneo, South Sumatra (Lampung), Java, Bali, Lombok, and Sulawesi |
| M. h. deignani | Southeast China (Guangdong, Hong Kong, and Hainan) and mainland Southeast Asia |
| M. h. dryas | Andaman and Nicobar Islands |
| M. h. jeanne | Philippines |
| M. h. peshwa | Central, West & Northeast India (Madhya Pradesh, Assam, Meghalaya, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu) (Moratelli et al., 2019) |
Local distribution map
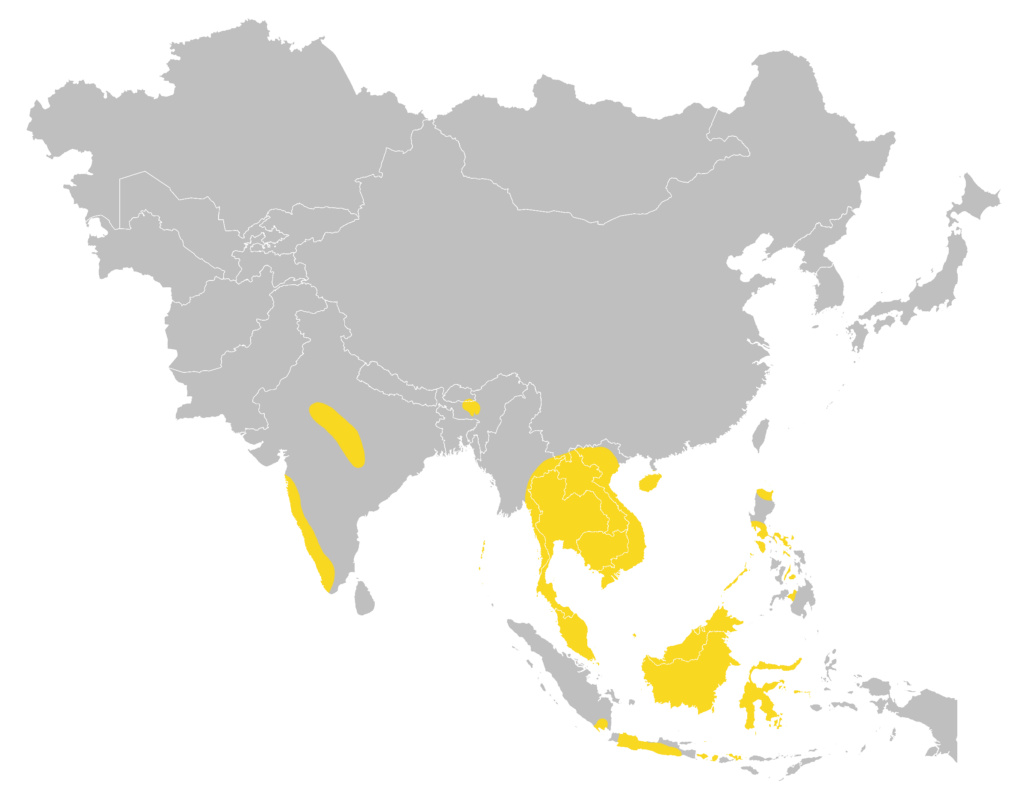
Global distribution map
(Moratelli et al., 2019)
Status and Conservation
| First record: | 1964 |
| Origin: | Native |
| Local status: | Rare (Shek & Chan, 2005) |
| National status: | Least Concern (Red List of China Vertebrates) |
| Global status: | Least Concern (IUCN Red List) |
| Potential threat: | TBC |
Echolocation

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Call structure | FM |
| Duration | 3.17 ± 2.60 ms |
| Inter pulse interval | 30.44 ± 24.10 ms |
| Peak frequency | 56.93 ± 7.98 kHz |
| Highest frequency | 134.25 ± 9.60 kHz |
| Lowest frequency | 38.38 ± 3.46 kHz |
|
Subspecies: |
M. h. deignani |
|
Region: |
Thailand |
| Method: | Hand release |
| Reference: | Hughes et al., 2011 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Call structure | FM |
| Duration | 2.57 ± 0.60 ms |
| Inter pulse interval | - |
| Peak frequency | 53.80 ± 5.14 kHz |
| Start frequency | 91.23 ± 15.27 kHz |
| End frequency | 41.60 ± 2.65 kHz |
|
Subspecies: |
M. h. peshwa |
|
Region: |
Southwest India |
| Method: | Hand release |
| Reference: | Wordley et al., 2014 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Call structure | FM |
| Duration | 3.27 ± 0.49 ms |
| Inter pulse interval | - |
| Peak frequency | 64.77 ± 3.91 kHz |
| Start frequency | 104.29 ± 5.13 kHz |
| End frequency | 42.28 ± 4.29 kHz |
|
Subspecies: |
M. h. dryas |
|
Region: |
India |
| Method: | Hand release |
| Reference: | Srinivasulu et al., 2017 |
Similar Species
Horsfield's Myotis
Myotis horsfieldii
Size:
Similar body sizes.
Color:
The dorsal fur displays a mottled pattern of dark grayish-brown coloration, while the ventral fur ranges from grayish-white to dark gray.
Ear pinna:
The upper portion of the anterior and posterior edges of the ear pinnae slightly narrows.
Tragus:
Slender, elongated, and overall relatively small in size.
Hindfoot:
Relatively large, with a length exceeding half the length of the tibia.
Wing membranes:
Connect to the base of the toes at a distance of approximately 2 mm from the ankle.
Whiskered Myotis
Myotis muricola
Size:
Similar body sizes.
Color:
The dorsal fur displays a uniform dark brown to blackish-brown coloration, while the ventral fur ranges from grayish-white to grayish-brown.
Ear pinna:
The upper portion of the anterior and posterior edges of the ear pinnae noticeably narrows, and there is a distinct notch in the middle section of the posterior edge.
Tragus:
Slender, conical, and overall narrower in shape.
Hindfoot:
Relatively smaller, with a length that is less than half the length of the tibia.
Wing membranes:
Connect to the base of the toes at a distance of more than 1 mm from the ankle.
Bibliography
Hughes, A. C., Satasook, C., Bates, P. J. J., Soisook, P., Sritongchuay, T., Jones, G., & Bumrungsri, S. (2011). Using Echolocation Calls to Identify Thai Bat Species: Vespertilionidae, Emballonuridae, Nycteridae and Megadermatidae. Acta Chiropterologica, 13(2), 447–455.
Jiang, Z. G., Jiang, J. P., Wang, Y. Z., Zhang, E., Zhang, Y. Y., Li, L. L., Xie, F., Cai, B., Cao, L., Zheng, G. M., Dong, L., Zhang, Z. W., Ding, P., Luo, Z. H., Ding, C. Q., Ma, Z. J., Tang, S. H., Cao, W. X., Li, C. W., Hu, H. J., Ma, Y., Wu, Y., Wang, Y. X., Zhou, K. Y., Liu, S. Y., Chen, Y. Y., Li, J. T., Feng, Z. J., Wang, Y., Wang, B., Li, C., Song, X. L., Cai, L., Zang, C. X., Zeng, Y., Meng, Z. B., Fang, H. X., & Ping, X. G. (2016). Red List of China’s Vertebrates. Biodiversity Science 24(5), 500‑551.
Lim, K. K. P., & Leong, T. M. (2014). New record of the Horsfield’s large-footed myotis in Singapore. Singapore Biodiversity Records, 2014, 106-107.
Moratelli, R., Burgin, C., Cláudio, V., Novaes, R., López-Baucells, A., & Haslauer, R. (2019). Vespertilionidae. In Mittermeier, R. A., & Wilson, D. E. (Eds.), Handbook of the Mammals of the World – Volume 9 Bats. (pp. 716-981). Lynx Edicions.
Shek, C. T. (2006). A Field Guide to the Terrestrial Mammals of Hong Kong. Friends of country park and cosmos book limited.
Shek, C. T., & Chan, C. S. M. (2006). Mist Net Survey of Bats with Three New Bat Species Records for Hong Kong. Hong Kong Biodiversity, 11, 1-7.
Srinivasulu, C., Srinivasulu, A., Srinivasulu, B., Gopi, A., Dar, T. H., Bates, P. J. J., Rossiter, S. J., & Jones, G. (2017). Recent surveys of bats from the Andaman Islands, India: diversity, distribution, and echolocation characteristics. Acta Chiropterologica, 19(2), 419-437.
Tanalgo, K. C., Achondo, M. J. M. M., Bretaňa, B. L. P., Casim, L. F., & Tabora, J. A. G. (2012). Wing ecomorphology and flight performance of bats in Pisan Caves, Kabacan, North Cotabato, Philippines. Asian Journal of Biodiversity, 3(1), 113-125.
Thong, V.D., Denzinger, A., Sang, N.V., Huyen, N.T.T., Thanh, H.T., Loi, D.N., Nha, P.V., Viet, N.V., Tien, P. D., Tuanmu, M. -N., Huang, J. C. -C., Thongphachanh, L., Luong, N. T., & Schnitzler, H. U. (2021). Bat Diversity in Cat Ba Biosphere Reserve, Northeastern Vietnam, A Review with New Records from Mangrove Ecosystem. Diversity 2021, 13, 376.
Wordley, C. F., Foui, E. K., Mudappa, D., Sankaran, M., & Altringham, J. D. (2014). Acoustic identification of bats in the southern Western Ghats, India. Acta Chiropterologica, 16(1), 213-222.
Hong Kong Bat Radar. (09/11/2025). A Field Guide to Bats of Hong Kong: Horsfield’s Myotis (Myotis horsfieldii ). https://hkbatradar.com/en/myotis_horsfieldii